Prime
A complete guide to your car fuses
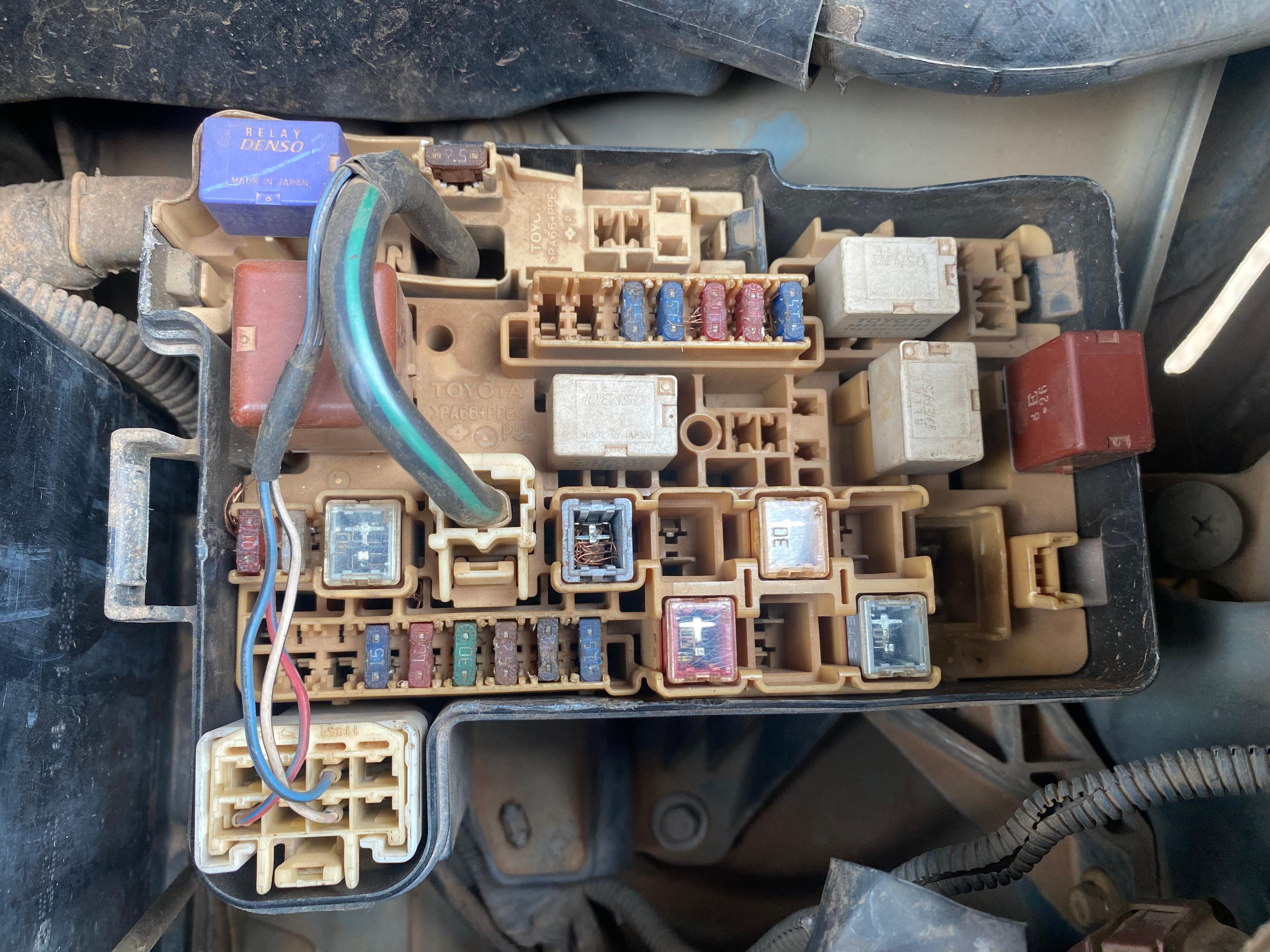
Car fuses are located in a fuse box often found in the engine compartment or under the dashboard. Photo/Daphine Nakabiri
What you need to know:
- Car fuses offer protection against overcurrent and short-circuiting, disconnecting the circuit if they detect a potentially dangerous level of current.
Just like the circuit breaker of your home’s electrical system turns off current flow in case of a short circuit,, car fuses do the same job for your vehicle to avoid damage.
Car fuses, also known as automotive fuses are devises that are dedicated to a specific electrical circuit to protect the vehicle’s electrical system from excessive current, which could damage other car components.
According to www.autobutler.com, car fuses are located in a fuse box often found in the engine compartment or under the dashboard. They are usually made up of a metal strip which is mounted between a pair of electrical terminals and enclosed by a plastic housing. When current exceeds a certain point in your vehicle’s components such as in the radio, a fuse acts as a safety device by breaking the circuit to prevent further damage to the car body or component itself.
Godfrey Ssebatta, a mechanic at Kimuuna Technical Services in Ttula, Kawempe Division Kampala, says car fuses play a crucial role in maintaining the safety and functionality of a vehicle’s electrical system, the reason they must be replaced once they are blown.While different vehicles have different types of fuses with a variance in appearance, they also have corresponding amperage ratings.
Blade fuses
These are the most common types and are found in modern cars. They are also called plug-in fuses. As they share a similar design with a coloured plastic body, they have two prongs that slot into the socket. Blade fuses have a flat and rectangular shape design and come in various ampere ratings that range from 1A to 40A, (A) representing an electric current of ampere/amps.
They also come in different categories such as the standard blade fuse also known as the automatic transfer case (ATC) used in most modern cars, the mini blade fuses also called the ATM used in domestic cars, trucks and SUVs. Other blades include the micro blade fuses, the low profile of the ATM and so on.
Glass tube fuses
Glass tube fuses are common in older vehicles that were made around the 1980s. They are cylindrical in nature with metal-end caps. In case of an overcurrent, the metal filament (which is a thin wire inside the tube) melts to prevent damage to the vehicle. Some common examples of glass tubes are 1AG, 3AG and 8AG, among others.
When choosing a car fuse, Ssebatta says it is essential to know the right kind of fuse basing on the electrical load that the fuse protects.
“For a safe and reliable operation of your vehicle’s electrical system, as a car owner, choose a fuse with the correct current rating to avoid damaging your car,” Ssebatta says, adding that different fuses handle different amounts of current. This means that if the amperage rating on the fuse you have chosen is too low, it will break too soon and if it is too high, components may fail to work.
How they work
Car fuses work as protective conductors during electrical processes that take place in the vehicle as they act as the weakest point in the circuit. When the current is too strong, the fuse element heats up and breaks to disconnect the circuit so that the electricity cannot flow through.
Typically, car fuses are made of a conductor of a thin strip of zinc or a metal with a low melting point. According to www.2carpros.com, during normal operation, when the current flowing through the circuit is within the rated limit of the fuse, the conductor remains intact, allowing the current to pass through the fuse without any issues.
However, when there is an overcurrent such as a short circuit or an excessive load in the circuit, the current flowing through the fuse increases and as it goes beyond the fuse’s rated capacity. The conductor inside the fuse begins to heat up due to the electrical resistance. Surpassing the critical threshold, the generated heat causes the conductor to reach its melting point, thus melting and breaking the circuit.
The air gap created within the fuse interrupts the flow of current through the circuit, preventing excessive current from affecting your vehicle’s components or causing any other damage.
How to tell if a fuse is blown
Since they are designed to protect cables, wires and electrical equipment from overcurrent and short circuits conditions, when they blow, they cause a loss of function for most components. They also trigger the check engine light, failure for the vehicle to start, an electrical smell or smoke and also melting of the fuse metal strip.
In the event that the housing of the fuse is transparent, this allows you as a car owner to notice whether the metal strip is melted or not. “If the metal strip inside the fuse is intact, it will appear as a continuous line. However, if the fuse is blown, the metal strip will be broken, creating a gap. Ssebatta explains.
Maintenance
Maintaining car fuses often involves you as a car owner understanding the vehicle’s electrical system and having periodic inspections for signs of damage or wear.
Fuses are typically single-use and relatively inexpensive compared to the potential cost of repairing or replacing damaged wiring, components, or even the entire electrical system. They, thus, provide cost-effective protection against electrical faults and, therefore, need to be replaced as soon as you notice they have blown, Ssebatta advises.
Also, while using a fuse with the wrong rating can compromise the protection of the circuit, car owners or mechanics must ensure they replace blown fuses with those of the same type and ampere rating to minimise potential harm.
Whereas moisture can lead to corrosion and compromise the effectiveness of the fuses, ensuring proper sealing of fuse boxes helps prevent this, ultimately protecting wiring connected to the fuse from damage, such as fraying.
Replacement
• Locate the car fuse box and then use its cover to identify the fuse corresponding to the malfunctioning electrical component. Fuses are usually labeled with a description of the circuit they protect.
• While the car ignition is turned off, carefully use a fuse puller to take out the blown fuse to avoid damaging the fuse or the fuse box. Do not touch any metal parts of the fuse or the fuse box with your fingers to avoid electric shock.
• Use a fuse with the same ampere rating to ensure proper protection. Finally, turn on the ignition and check if the electrical component is associated with the replaced fuse.




