Prime
Uganda registers four Mpox recoveries, zero deaths
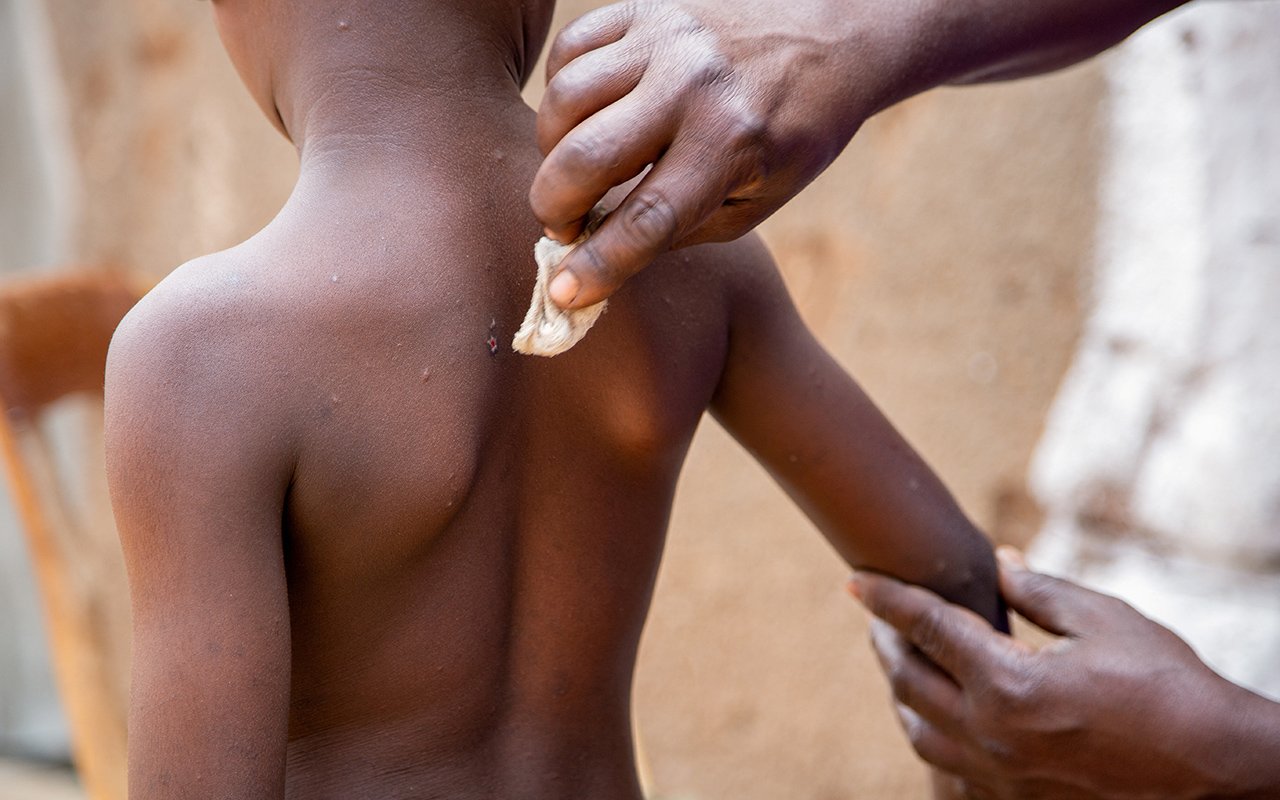
A man shows the marks on the skin of his six-year-old son after he recovered from mpox in Bujumbura, Burundi on August 28, 2024. PHOTO/ REUTERS
What you need to know:
- Dr Aceng reassured the population that there is no cause for alarm and that the Ministry of Health is in full control of the situation.
The Health Ministry has announced that four Mpox patients have recovered, demonstrating the country's capability to manage the viral disease.
Dr Jane Ruth Aceng, the Health Minister, said the quadruple is part of the 10 confirmed cases of the disease in the country. The country has not reported Mpox death.
"Out of these 10 cases, four individuals have since recovered, while six are currently receiving care at the National Isolation Facility in Entebbe. Additionally, a total of forty-nine (49) contacts of the confirmed cases have been identified and are under close monitoring," she said on Friday in Kampala.
Dr Aceng reassured the population that there is no cause for alarm and that the Ministry of Health is in full control of the situation.
"I would like to reassure all tourists, investors, and traders intending to visit Uganda that the country remains very safe for travel and trade. There is no cause for alarm."
The Ministry reported that Kasese District has three cases, Mayuge District (3), Kampala (2), Wakiso District (1), and Amuru District (1). Most confirmed cases (60 per cent) are male, and 40 per cent are female, with over 40 per cent of affected individuals falling within the 30-39 year age bracket.
The viral disease, first reported in Uganda in July 2024, spreads through close physical contact, sexual intercourse, and sharing clothes or materials touched by an infected person. Symptoms include fever, body weakness, skin rash, blisters, and pus-filled sores on the skin.
To prevent the spread of Mpox, Dr Aceng emphasised the importance of avoiding physical contact, washing hands regularly with soap and water, avoiding sharing clothes and beddings, and avoiding sexual intercourse with unknown partners.
According to information from the Health Ministry, if one develops symptoms, particularly after recent travel overseas or contact with a case, including sexual contact, they should seek care from a general health practitioner or nearest sexual health clinic.